-
Goals of the course
Underlining the processes for designing effective and efficient instruction.
Developing knowledge and skills for instructional analysis, design, development, implementation and evaluation phases of instructional design.
Developing an understanding of the instructional technologies in language learning
-
What is Instruction?
Delivery of information & activities that facilitate learners’ attainment of intended, specific learning goals. Activities focused on learners learning specific things.
Instruction is the conduct of activities that are focused on learners learning specific things.
Education-very broad term describing all experiences in which people learn. Many are unplanned, incidental, and informal. All instruction is education, but not all education is instruction.
Training-refers to instructional experiences focused on acquiring specific skills that will normally apply almost immediately.
Teaching-refers to learning experiences in which the instructional message is delivered by a human being.
-
Teaching?
Learning experiences in which the instructional message is delivered by a human being-not a videotape, textbook, or computer program—but a live teacher.
All learning experiences in which the instructional message is conveyed by other forms of media is instruction.
-
Learning & Environment
It is not only the place where teaching is done, but the methods, tools and materials to be used in passing the information and guiding the learners.
We need to use materials in learning environment
-
What is Technology?
Greek: “Technos” or Know-how.
A Device or a Method
Electronic or Mechanical
In its simplest sense, technology is the act of transforming theoretical knowledge and scientific laws into practice Technology is a rational discipline designed by human beings to build superiority over nature (Simon, 1983).
Then, Is science always designed to dominate nature?
The Assumption about the technological advances? The things we create are the tools that help us to cope with the natural environments and meet the needs of life. This traditional explanation emphasizes the importance of necessity and utility (Basalla, 1996)
-
NECESSITY????
What led the automobile inventors was not the necessity… there was no horse shortage!
In fact, in the first decade (1895-1905), the car was seen as a toy, or an amusement vehicle, not as a means of transportation.
Same is true for trucks!
The need for a truck was not before, but after its invention.
-
Technology
The invention is not based on the heroic efforts of several geniuses; it is a social process that happens with the accumulation of many small progressives.
-
Technology and Science
Science is the knowledge of how nature works (the laws of nature), while technological knowledge aims at utilization and application.
-
What is Instructional/Educational Technology?
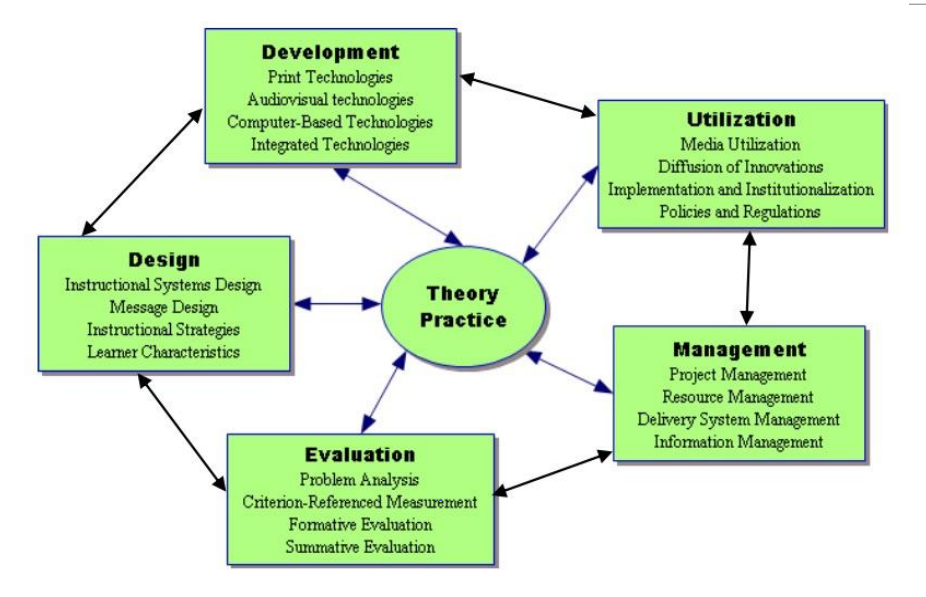
"Instructional Technology is the theory and practice of design, development, utilization, management and evaluation of processes and resources for learning.” (Seels & Ritchey, 1994)
◦ Theory and practice,
◦ Design, development, utilization, management and evaluation
◦ Processes and resources
◦ Learning
-
Five Domains of Instructional/ Educational Technology?
-
-
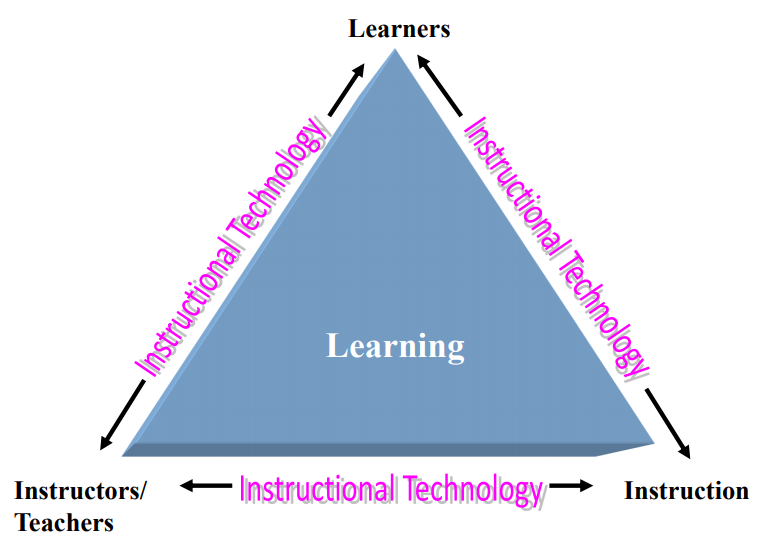
Relationship among learners, teacher, instruction and instructional technology
-
Knowledge Sources
- Research/developments in technology (computer science)
- research in human learning (education, psychology)
- development of new instructional procedures (education)
- communication theory
- human/computer interaction (psychology)
- information design (information sciences)
- visual and audio design (art, music)
-
Instructional Media
From Latin that means “between”. Any channel that carries the information between source and receiver. Most of the time media are tangible.
Instructional media encompasses all the materials and physical means an instructor might use to implement instruction and facilitate students' achievement of instructional objectives.
This may include traditional materials such as chalkboards, handouts, charts, slides, overheads, real objects, and videotape or film, as well newer materials and methods such as computers, DVDs, CD-ROMs, the Internet, and interactive video conferencing.
-
Araç-Gereç
Öğrenme öğretme sürecinde kullanılan ve bu süreci destekleyen kaynak, materyal, görsel, işitsel, teknolojik ve güncel olan her şey araç ve gereçtir.
-
Araç-Gereç kavramları
Araç-gereç: Öğretme, öğrenme etkinliklerinde kullandığımız yardımcı kaynaklar araç-gereç ikilisinden oluşur.
Araç: Daha çok mekanik nitelikteki yardımcı olup; gereci sunmada vazgeçilmez ögedir. Örnek: Tepegöz, bilgisayar, televizyon
Gereç ise; daha çok yazılı basılı nitelikteki yardımcı olup, aracın vazgeçilmez ögesidir. Örnek: Tepegöz asetatı, bilgisayar ve televizyon programları.
-
History of Educational Technology
Education technology begins when people ask the first question, "How do I learn it? (Çilenti, 1988).
-
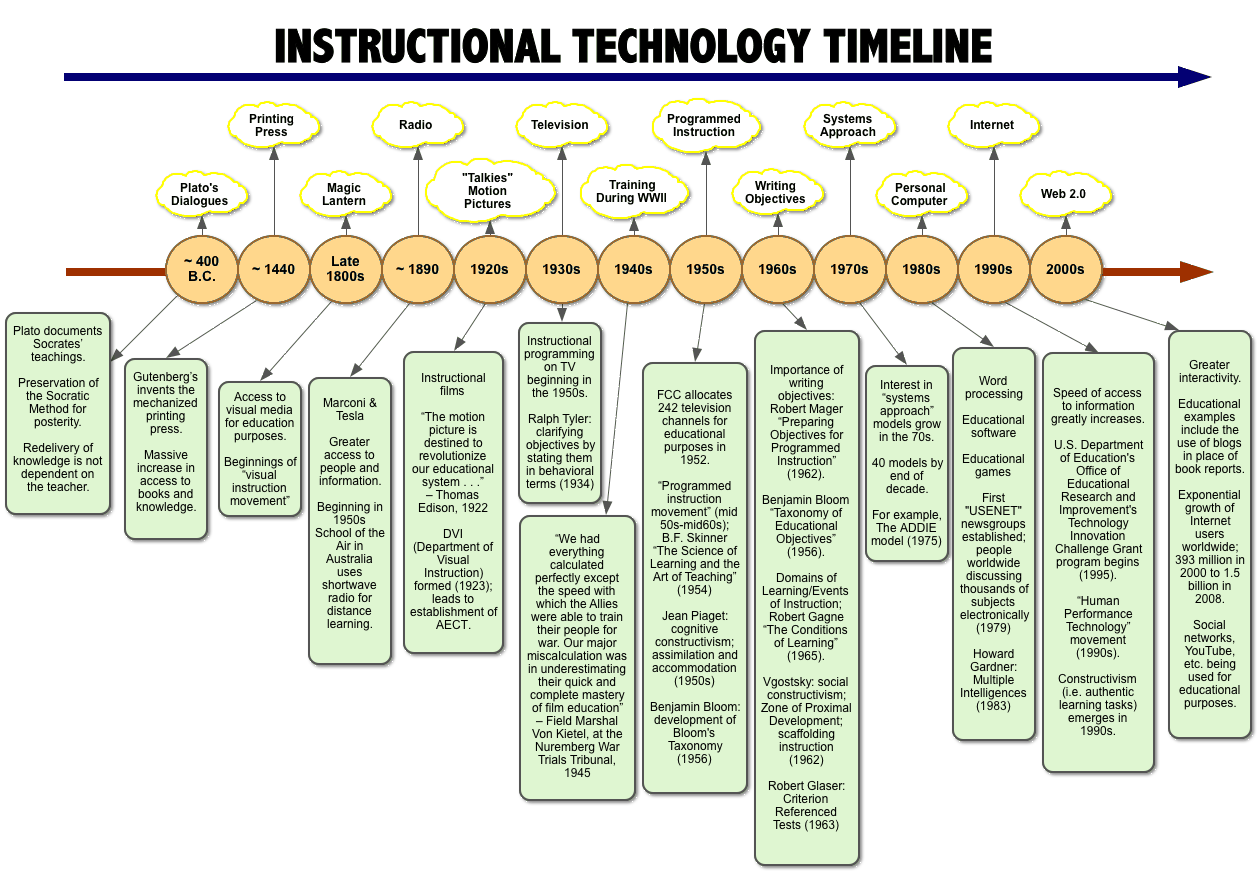
Historical Timeline.
1905 - 1st school museum in St. Louis.
1908 - Visual Instruction movement begins.
1910 - 1st catalog of Instrucational films.
1920 - Birth of instructional fiıms.
1941 - WW II training films
1953 - Use of television in education.
1974 - Advent of the Personal Computer.
1985 - World's first graphing calculator
2004 - Podcating
1940's - WW II Thousands of soldiers rapidly trained
1950's - B. F. Skinner - Behaviorism and Operant Conditioning
1950's - Benjamin Bloom - Learning Taxonomy
1960's - Robert Gagne - Conditions of Learningi
1970's - David Merril - Component Display Theory
1980's - Thomes Gilbert - Perfomance Technology
2000 - Online and Web Based Instruction
-
Instructional Technologe timeline
-
Systems theory
Seminal work in instructional design arises from systems theory.
◦ Challenges reductionism – a system is greater than the sum of its parts.
General System Theory - a set of interrelated parts all working together to achieve a common goal. A general system is inherently a closed one, which leads to stability.

